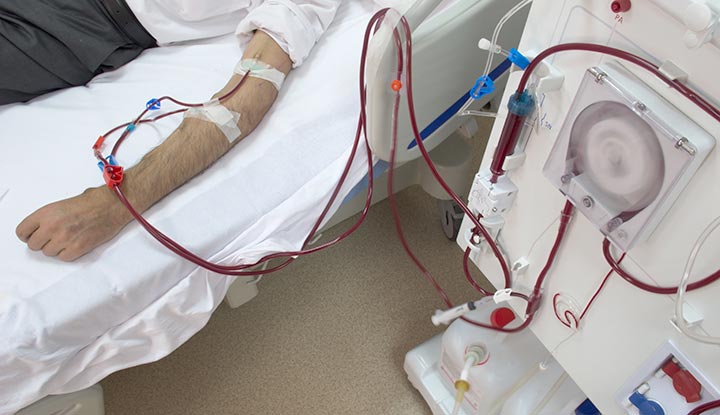
Chronic kidney disease affects millions globally, with many needing dialysis for survival. Effective dialysis access relies heavily on proper vascular access, which connects the patient’s circulatory system to the dialysis machine. These access procedures create and maintain pathways for blood removal and return during treatment. Understanding the associated risks and benefits helps patients and healthcare providers choose the most suitable access method for their specific situations.
Types of Dialysis Access
Healthcare providers utilize three primary types of dialysis access, each with distinct characteristics and applications. Arteriovenous fistulas represent the preferred access method, created by surgically connecting an artery directly to a vein, typically in the forearm or upper arm. This connection allows the vein to enlarge and strengthen over time, supporting repeated needle insertions.
Arteriovenous grafts serve as an alternative when natural veins are unsuitable for creating a fistula. These procedures involve placing a synthetic tube between an artery and a vein, creating an artificial pathway for blood flow. Central venous catheters provide immediate access by inserting a catheter into large veins in the neck, chest, or groin area.
Risks Associated with Access Procedures
Dialysis access procedures, although necessary for treatment, carry certain risks that patients should be aware of before undergoing them. Here is a list of potential complications associated with these procedures:
- Infection: One of the most serious risks, particularly with central venous catheters. Bacterial contamination at the insertion site or in the bloodstream can lead to systemic complications that require immediate medical attention.
- Bleeding: This can occur during or after the procedure, especially in patients taking anticoagulant medications.
- Blood Clots: Clots may develop within the access site, reducing blood flow and compromising the effectiveness of dialysis.
- Stenosis: Narrowing of blood vessels may occur, potentially requiring additional procedures to restore proper blood flow.
- Vascular Complications:
- Steal Syndrome: A condition where blood flow is diverted away from the hand, causing circulation issues.
- Aneurysm Formation: Abnormal enlargement of the blood vessel at the access site, which may require surgical revision or replacement of the access.
Benefits of Dialysis Access Procedures
Properly functioning dialysis access plays a role in improving treatment outcomes and patient well-being. It can aid in effective dialysis, reduce complications, and enhance overall quality of life. Here are some benefits of reliable dialysis access:
- Efficient Toxin and Fluid Removal: Adequate blood flow rates enable effective clearance of toxins and excess fluid, contributing to better overall health and fewer complications from inadequate dialysis.
- Long-Term Durability: Arteriovenous fistulas often last for years with proper care, minimizing the need for repeated procedures and hospitalizations. This leads to lower healthcare costs and less disruption to daily life.
- Improved Quality of Life: Reliable access supports consistent dialysis schedules, reducing treatment delays and complications. This allows patients to adhere to treatment plans and achieve better clinical outcomes.
Strategies for Managing Risks and Benefits
Successful dialysis access management requires thorough planning and ongoing monitoring to provide optimal outcomes. Pre-procedural evaluation assesses vascular anatomy, medical history, and risk factors to determine the ideal access type and timing. Post-procedural care includes regular monitoring for complications, patient education on hygiene and activity, and follow-up appointments to detect issues early. Physical exams and diagnostic tests, like ultrasounds, help identify problems early, allowing for timely intervention and preserving access to function.
Make Informed Treatment Decisions
Dialysis access procedures are necessary for kidney replacement therapy, with each type offering unique pros and cons based on individual needs and treatment goals. Healthcare providers collaborate with patients to create personalized plans that maximize outcomes and minimize complications through regular monitoring and timely care. For expert guidance tailored to your medical needs, consult a qualified nephrologist or vascular surgeon today.