The health of our feet is integral to our comfort and daily activities, yet certain conditions can disrupt this balance. One such condition is ingrown toenails. For individuals experiencing this issue, it can lead to discomfort during routine tasks such as walking or wearing shoes.
What Are Ingrown Toenails?
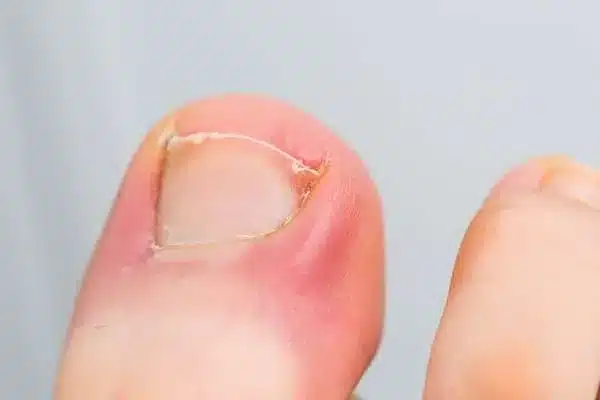
Ingrown toenails occur when the edge or corner of a toenail grows into the surrounding skin rather than over it. This growth leads to irritation and sometimes escalates to localized inflammation. The condition typically affects the big toe but also develops in other toes depending on nail growth patterns and external factors. The causes of ingrown toenails are varied. Tight or improper footwear, incorrect trimming of toenails, and repetitive pressure on the toes from physical activities are common factors. While ingrown toenails can often be an isolated condition, if ignored, they may lead to further issues, such as skin irritation or infections, emphasizing the necessity to monitor symptoms early on.
What Are the Symptoms?
The symptoms of ingrown toenails can vary in severity and evolve over time. Early stages may present with mild discomfort or tenderness around the affected nail. As the condition progresses, the following signs may appear:
- Pain and Tenderness: Often felt along one or both sides of the toenail, pain may intensify while walking or applying pressure.
- Redness and Swelling: The skin surrounding the toenail may appear red or swollen due to irritation caused by the nail pressing into it.
- Discharge or Infection: When the skin is pierced, it creates an entry point for bacteria or fungi, leading to infection. This may result in additional swelling, pus, or changes in skin coloration around the nail.
These symptoms can impact daily mobility and comfort levels. Remaining attentive to how the affected area feels and monitoring any progression can be useful in determining whether further steps are necessary.
How Are They Treated?
Treatment for ingrown toenails ranges from at-home care to professional interventions, depending on the severity of the condition. Early-stage symptoms often respond well to general care practices, while more advanced cases require evaluation by a medical professional.
At-Home Care
For minor cases, at-home methods can provide relief and promote healing. Submerging the foot in warm water multiple times a day may help reduce discomfort and allow the skin to soften. Opting for shoes or socks that do not compress the toes may prevent further aggravation of the condition. If engaging in home care, it is always wise to observe the affected area for any changes that warrant professional attention.
Professional Treatments
It is not uncommon for medical practitioners to provide tailored advice for preventing recurrences, such as guidance on nail trimming techniques or recommending proper footwear. When ingrown toenails cause persistent discomfort or develop complications, professional care may be required. Treatment approaches include:
- Nail Trimming and Lifting: A healthcare provider can carefully lift or remove the nail portion lodged into the skin to ease discomfort and prevent further irritation.
- Partial or Full Nail Removal: For recurrent or severe cases, partial nail removal may be advised. This procedure involves removing the ingrown portion of the toenail.
- Treatment of Infection: If an infection is present, additional interventions, such as topical or oral treatments, are used to promote recovery and address inflamed areas effectively.
Speak to a Foot Specialist
Although ingrown toenails are a common occurrence, they can cause discomfort and, in certain cases, lead to additional concerns. If you experience ongoing pain, swelling, or signs of infection, contacting a foot specialist can provide a clear path forward. Professional insight helps assess the condition accurately and recommend treatments best suited to your situation.