A periodontist is a dental specialist who focuses on preventing, diagnosing, and treating gum-related issues and diseases that affect the supporting structures of your teeth. Their expertise often extends to managing severe gum disease and performing surgeries like grafts and implants. Here’s more information on gum disease:
What Is Gum Disease?
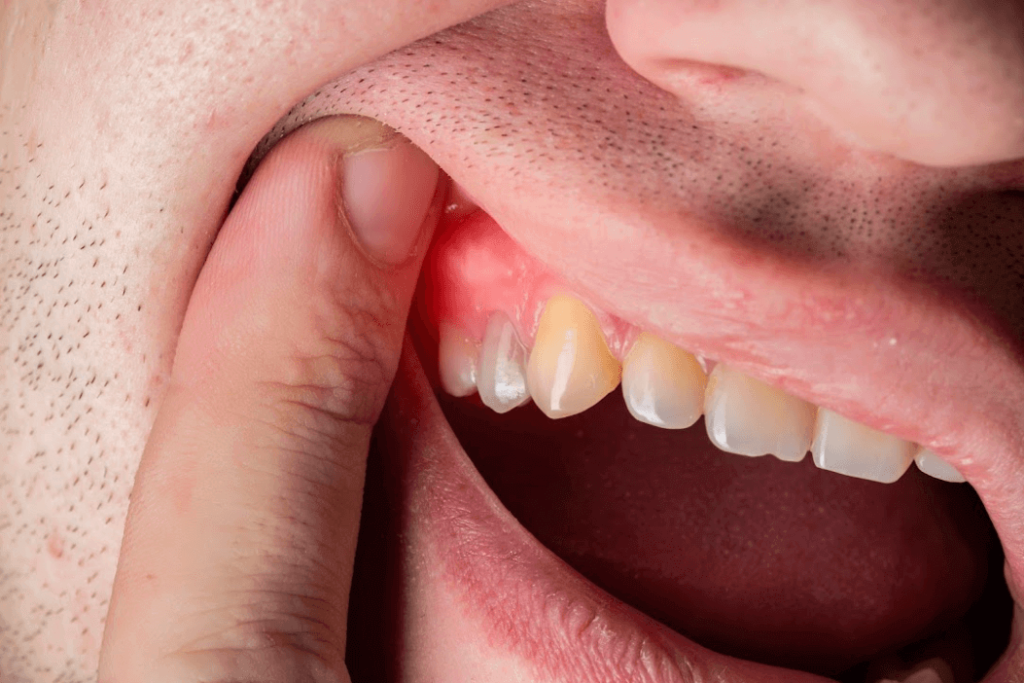
Gum disease, medically referred to as periodontal disease, is a condition that affects the gums and supporting tissues in the mouth. Left untreated, it may compromise the stability of teeth and contribute to other dental complications that a periodontist can help treat. The condition typically starts with gingivitis, an inflammation of the gums caused by bacterial plaque buildup.
Early detection is key to managing the infection. Common signs of gum disease include red or swollen gums, bleeding during brushing or flossing, persistent bad breath, and gum recession. While gingivitis is reversible with proper care, untreated gum disease may progress to periodontal disease, a more severe stage that jeopardizes the bone and connective tissue supporting the teeth.
What Causes Gum Disease?
Gum disease results from a variety of factors, most of which center around poor oral hygiene. Other contributors include genetics, smoking, certain medications, and health conditions like diabetes. Here are some different gum disease conditions and how you can manage gum disease at home:
Treating Gum Disease Conditions
By identifying these stages of infection, periodontists determine the appropriate preventative and corrective approaches for treatment. The three stages of gum disease are:
- Gingivitis: The mildest form of gum disease, marked by gum inflammation without affecting the bone or deeper tissues. Symptoms often include mild swelling and bleeding, particularly when brushing or flossing. This stage is reversible with good oral hygiene practices.
- Moderate Gum Disease: Builds on untreated gingivitis, wherein bacteria invade beneath the gum line. This stage leads to more pronounced gum recession, discomfort, and the onset of bone loss. Treatment at this stage often requires professional cleaning, such as scaling and root planing.
- Severe Gum Disease (Periodontitis): The most advanced stage of infection, where significant destruction has occurred. Symptoms include deep periodontal pockets, advanced bone loss, and noticeable tooth mobility. This stage demands intensive interventions, sometimes including surgery, to manage.
Preventing Gum Disease
Preventing gum disease starts with consistent and effective oral hygiene. Following these steps helps to protect your gums and improve your overall dental health:
- Brush Twice Daily: Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste to clean your teeth twice a day. Be sure to angle the brush toward the gum line to remove plaque effectively.
- Floss Regularly: Flossing removes the plaque and debris that brushing alone can’t reach, particularly between teeth.
- Rinse With an Antimicrobial Mouthwash: A mouthwash designed to reduce bacteria can add another layer of protection.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking not only stains teeth but also impairs gum health by reducing the blood flow to the gums, slowing healing processes.
- Schedule Regular Dental Checkups: Routine cleanings and early detection of gum problems may prevent issues from escalating.
How Does Infection Spread?
When gum disease advances, it doesn’t remain confined to the gums. The condition can lead to other significant dental issues if not addressed in a timely manner. The bacteria responsible for gum infections can begin to break down the bone that supports your teeth, eventually causing them to loosen or fall out. Bone loss and tooth decay occur more as infection spreads to soft tissues and bone in the mouth.
The spread of harmful bacteria creates an environment where cavities are more likely to form. Gum infections can also lead to the development of abscesses, which are painful pockets of pus that form between the teeth and gums. This cascade of issues highlights how untreated gum disease can weaken oral health over time, causing complications.
Schedule a Visit With a Periodontist
While diligent at-home care is helpful, professional intervention remains a necessary component of managing and preventing gum disease. Periodontists can provide specialized care tailored to the severity of your condition, from deep cleanings to surgical solutions. Regular visits with dental professionals help detect early signs of gum disease, enabling you to maintain optimal oral health. Take a proactive approach to your oral health and contact a dentist today.